Microsoft made its newest operating system, Windows 11, publicly available on October 5, 2021 — a little more than six years after Windows 10 debuted. Windows 11 offers updates and new features, including a simpler design intended to increase productivity, ways to connect to people faster, an all-new Microsoft Store, and a more open ecosystem that unlocks new opportunities for developers and other creators.
This Microsoft Windows 11 cheat sheet details the operating system’s main features, lists system requirements, explains how and when to get it, and more.
What is Windows 11?
Windows 11 is Microsoft’s newest major release of its operating system and the successor to Windows 10. The OS features an all-new simplified yet modernized interface designed to inspire productivity and creativity.
While the March 2022 Windows 11 Patch is not classified as a “feature update” to the operating system by Microsoft, the patch did contain a few unannounced features. For example, if you run Windows 11 with Widgets turned on, you will notice a new icon in the lower left corner of the desktop that provides a summary of your local weather conditions. Microsoft also updated Notepad and rebranded the Groove media player.
As of May 2024, Windows 11 is the second most popular Windows version in use after Windows 10.
What is the Windows 11 version timeline?
Version 21H2
The original version of Windows 11 was released to the public in October 2021. This version, also referred to as version 21H2 and codenamed “Sun Valley,” was made available as a preview build to Windows Insiders in the development channel in June 2021. During its approximately one year existence, Windows 11 version 21H2 was updated and patched over two dozen times.
Version 22H2
The Windows 11 2022 Update, often referred to as 22H2 and codenamed “Sun Valley 2,” was the first major update to Windows 11. The first preview of this version of Windows 11 22H2 was released to Windows Insiders in the Dev Channel on September 2, 2021. The update began rolling out to the public on September 20, 2022.
The Windows 11 2022 Update included several feature updates, improvements and enhancements. These included hypervisor-protected code integrity security, sync status of OneDrive displayed in File Explorer, Windows Studio Effects, and streamlining changes for future Windows 11 updates and patches. Since its release, Windows 11 22H2 has been patched and updated numerous times.
SEE: Check out these Windows 11 22H2 enterprise features you need to know.
Version 23H2
The Windows 11 2023 Update, often referred to as 23H2, was released to the public with eligible computers on September 26, 2023. In September 2023, Microsoft began rolling out a new Windows 11 update to eligible computers. Known as Windows 11 23H2, this latest major update adds new features, applications and security protocols to the operating system, including Windows Copilot, File Explorer enhancements, Windows backup app, taskbar improvements, new volume mixer, 7-Zip and RAR support and RGB peripheral customization.
SEE: Everything you need to know about Microsoft Copilot in this TechRepublic cheat sheet.
Version 24H2
The Windows 11 24H2 Update is an upcoming update to the operating system. A preview was released through the Windows Insider Program to developers on February 8, 2024. Some notable enhancements will include HDR Backgrounds, Wi-Fi 7 support, AI Voice Clarity and AI CoWriter in Notepad.
What new features come with Windows 11?
New Start layout
In Windows 11, the newly centered Start button uses the cloud and Microsoft 365 to show recent files, no matter what platform or device they were being viewed on previously, including an Android or iOS device.
Snap Layouts, Snap Groups and Desktops
A new set of features in Microsoft Windows 11 is the introduction of Snap Layouts, Snap Groups and Desktops. These offer a “powerful way to multitask and stay on top of what you need to get done,” according to Microsoft’s press release. With these Windows 11 features, users can organize windows and optimize screen real estate for a cleaner visual layout (Figure A). Users can create and customize separate Desktops for each part of their life — like one for work and one for personal use.
Figure A
Chat from Microsoft Teams
In Windows 11, Microsoft integrates Chat from Microsoft Teams into the taskbar, so users can instantly connect via text, chat, voice or video with personal contacts, regardless of which platform or device is being used across Microsoft Windows, Android or iOS. Through Microsoft Teams, users can now instantly mute and unmute or start a presentation directly from the taskbar in the new OS.
Lockscreen Widgets
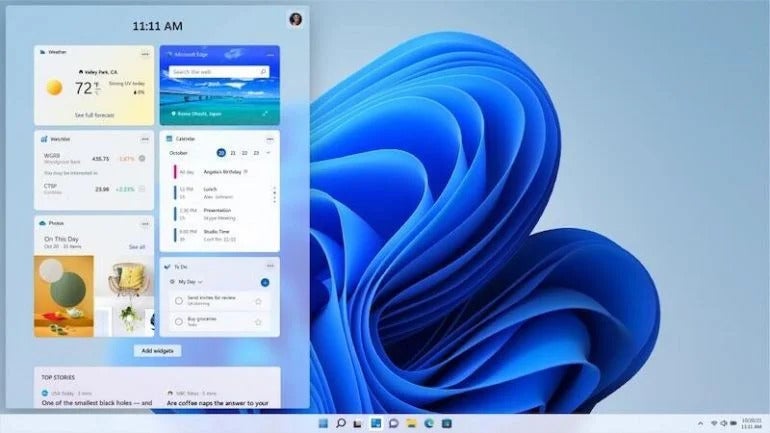
Windows 11’s new Widgets are a personalized feed powered by artificial intelligence and Microsoft Edge. Instead of using a phone to check news, weather or notifications, now users can open their Windows 11 desktop to see a similarly curated view (Figure B). Widgets offers new opportunities within Windows 11 to deliver personalized content for creators and publishers.
Figure B
Microsoft Store overhaul
The Microsoft Store has undergone a major overhaul; users now have one safe location for apps and content to watch, create, play, work and learn. According to Microsoft, the Store “has been rebuilt for speed and with an all-new design that is beautiful and simple to use. Not only will we bring you more apps than ever before, we’re also making all content — apps, games, shows, movies — easier to search for and discover with curated stories and collections.”
Leading first- and third-party apps such as Microsoft Teams, Visual Studio, Disney+, Adobe Creative Cloud, Zoom and Canva have also been added to the Microsoft Store.
Android apps
Through its partnership with Amazon and Intel, the Microsoft Store allows users to discover Android apps, which can be downloaded via the Amazon Appstore. Microsoft is enabling developers and independent software vendors to bring apps to the Microsoft Store, no matter what app framework is used to create them.
What new features come with Windows 11 22H2?
The first major content patch, known as Windows 11 22H2, added several new features and applications to the operating system.
For enterprise users, Windows 11 22H2 improved File Explore functionality to integrate OneDrive status, which improves team collaboration and cooperation. The update also added a new feature called Windows Studio Effects, which will improve virtual meetings with AI-powered processing efficiency.
At the user level, Windows 11 22H2 added new quality-of-life features like voice activated navigation, Start Menu feature improvements, additional personalization themes and the Clipchamp app. Further, Windows 11 22H2 added new live captioning features for automatically transcribing virtual meetings.
What new features come with Windows 11 23H2?
The latest major content patch, known as Windows 11 23H2, adds several new features and applications to the operating system.
The highlight of Windows 11 23H2 Update is the addition of Windows Copilot, which integrates an on-demand generative AI feature directly into the operating system. Windows Copilot will be accessible to users as they work with Mail, Paint, Notepad and any other Windows app.
Windows 11 23H2 includes the often asked for ability to control RGB peripherals natively through Windows settings instead of relying on third-party software and utilities. The update also supports several common open-sourced archiving protocols, including 7-Zip and RAR. The 23H2 update includes quality-of-life improvements for Windows File Explorer and the taskbar.
SEE: How to Enable Windows Copilot in Windows 11 23H2
What AI features have been added to Windows 11?
Microsoft has added a number of features based on artificial intelligence to Windows 11 since its initial release, including Live Captions, background noise removal in videoconferencing, webcam autoframing and the Bing Chat chatbot in the taskbar’s search field.
Copilot
In January 2024, Microsoft announced that the new Windows 11 PCs, including the Surface line coming out through Spring 2024, will include a Copilot key. The Copilot key enables easy access to Microsoft’s AI assistant, Copilot, in Windows.
Copilot assists with a variety of tasks, such as transforming documents into presentations, editing photos, summarizing emails and meetings, managing PC settings like enabling battery saver and accessing information from different apps and platforms.
SEE: Windows 11 Update Brings New Tricks to Microsoft Copilot
Recall
Recall, announced at Microsoft Build on May 20, 2024, is a new AI-powered feature that allows users to quickly and intuitively search through their device’s history using natural language questions. While this is included as a part of Windows 11, it will only work on Copilot+ PCs that have built in neural processing units.
Recall runs locally, logging everything the computer has done, including web browsing, file creation and voice chats, so anything the user has come across via that PC can be called upon. Recall is incorporated with Timeline — the existing Windows feature that shows running apps and past activities — to give an easy-to-use scrollable interface.
How to disable Recall
Recall has proven a controversial feature since it was announced, primarily due to privacy and security concerns. Microsoft has since made it an opt-in feature rather than being enabled by default, and committed to enhancing the security measures around the data it stores.
Despite this, the tech giant delayed Recall’s rollout with the new Copilot+ PCs on June 18, 2024, so it can “ensure the experience meets our high standards for quality and security.”
While Recall is still unreleased, some members of the Windows Insider program have had the chance to explore a preview version of the feature and have shared how it can be disabled.
- Open Windows Settings and navigate to Privacy & Security in the sidebar.
- Select Recall & Snapshots to view the Recall settings.
- Click Delete Snapshots and then Delete All to clear Recall’s history.
- Click the Save Snapshots switch to turn it to the Off settings to disable Recall.
What do developers need to know about Windows 11?
PWABuilder3
Windows 11 features the new PWABuilder3, so developers can build a PWA from their web app in minutes (Figure C). WebView2 runtime is included with Windows 11, which makes it easier to take advantage of its web platform as a secure way to build hybrid web apps. Offerings like Windows Terminal and the new Microsoft Edge DevTools can still be used, as they are now included in Windows 11.
Figure C
Windows App SDK
Released March 29, 2021, the Windows App SDK, previously known as Project Reunion, makes it easier to integrate Windows 11 features into apps, but it still allows developers to reach more than a billion users on Windows 10.
Windows on ARM
Developers can build apps that run natively on Windows on ARM with the new ARM64 Emulation Compatible ABI. Using the ARM64EC, native ARM and emulated x64 code can be mixed in the same process or module. This interoperability means developers can optimize apps to run on Windows on ARM — even if the app has x64 dependencies or loads x64 plugins they don’t control.
WinUI3
To rejuvenate app designs, developers can use WinUI3 in Windows 11, which offers built-in UI updates such as rounded geometry, refreshed iconography, new typography, fun micro-interactions like Lottie animation and refreshed color palette. The Snap layouts feature will help with maximum productivity in Windows 11.
Reunion Windowing
Reunion Windowing allows developers to easily manage and create app windows. The feature works with existing app codes, simplifies common operations and brings new functionality to desktop apps like Light-Dismiss Behavior, Picture-In-Picture mode and easier titlebar customization.
SEE: Learn how to install Windows 11 from Microsoft’s ISO file.
Microsoft Store commerce availability
Along with the major changes to the Microsoft Store, Microsoft is taking steps to unlock greater economic opportunity for creators and developers. Microsoft now allows developers and independent software vendors to advertise their apps on the platform regardless of whether they’re built as a Win32, Progressive Web App, Universal Windows App or any other app framework, so they can reach and engage a larger audience.
The revenue share policies have changed, too. Developers can now bring their own non-gaming apps into the Microsoft Store with their own commerce platform and keep 100% of the revenue — Microsoft takes nothing. Developers can still use Microsoft’s commerce platform, with competitive revenue share of 15% for apps and 12% for games.
Is Windows 11 free?
Windows 11 is available through a free upgrade for eligible Windows 10 PCs and on new PCs as of October 5, 2021. To see if your Windows 10 PC is eligible for the free upgrade to Windows 11, download the PC Health Check app.
Train your team and become a Windows 11 power user with The Essential Windows 11 Course and The Ultimate Windows 11 Training Video Course from TechRepublic Academy.
How do I upgrade to Windows 11?
Microsoft Windows 11 is available as a general release to the public. Assuming your personal computer meets the prerequisite requirements, including installation of Windows 10 1909 or later, you can upgrade to Windows 11 by navigating to the Update & Security settings screen.
Users may also take advantage of the Windows 11 Installation Assistant to bypass the Windows 10 Update & Security screen and upgrade to Windows 11 directly.
Can you set up Windows 11 without a Microsoft Account?
Microsoft requires the user to log in to a free Microsoft account to download and install Windows 11; however, this step can be avoided by creating a local account — i.e., one that only applies to that machine and does not involve an internet connection — during the setup process.
Follow these steps to create a local account and install Windows 11.
- Follow the Windows 11 installation process until you are presented with the Let’s Connect You To A Network box.
- Press Shift + F10 to open command prompt, type “OOBE\BYPASSNRO” and press enter. The PC will reboot.
- Restart the installation process. When you reach the Let’s Connect You To A Network box, click I Don’t Have Internet and then Continue With Limited Setup.
Create a local account when prompted, and then finish the installation. You can connect to the internet once the installation has completed.
Why is my PC not eligible for Windows 11?
To install Windows 11, your PC must meet system requirements that it may not currently satisfy. These requirements include:
- Processor: 1GHz or faster with two or more cores on a compatible 64-bit processor or System on a Chip.
- RAM: 4GB.
- Storage: 64GB or larger storage device.
- System firmware: UEFI, Secure Boot capable.
- Graphics card: Compatible with DirectX 12 or later with WDDM 2.0 driver.
- Display: High-definition (720p) display that is greater than 9″ diagonally, 8 bits per color channel.
- Internet connection: Windows 11 Home edition requires internet connectivity and a Microsoft account to complete device setup on first use. Switching a device out of Windows 11 Home in S mode requires internet connectivity.
SEE: Here’s how to tell if your PC can run Windows 11.
What are the feature-specific requirements for Windows 11?
Some features in Windows 11 have increased requirements beyond those listed above. Here are additional details regarding requirements for key features per Microsoft.
- 5G support: Requires a 5G-capable modem.
- Auto HDR: Requires an HDR monitor.
- BitLocker to Go: Requires a USB flash drive (available in Windows Pro and above editions).
- Client Hyper-V: Requires a processor with second level address translation capabilities (available in Windows Pro and above editions).
- Cortana: Requires a microphone and speaker and is currently available on Windows 11 for Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Spain, the U.K. and the U.S.
- DirectStorage: Requires an NVMe SSD to store and run games that use the Standard NVM Express Controller driver and a DirectX12 GPU with Shader Model 6.0 support.
- DirectX 12 Ultimate: Available with supported games and graphics chips.
- Presence: Requires a sensor that can detect human distance from device or intent to interact with device.
- Intelligent Video Conferencing: Requires video camera, microphone and speaker for audio output.
- Multiple Voice Assistant (MVA): Requires a microphone and speaker.
- Snap: Three-column layouts require a screen that is 1920 effective pixels or greater in width.
- Mute and Unmute from Taskbar: Requires video camera, microphone and speaker for audio output.
- Spatial Sound: Requires supporting hardware and software.
- Teams: Requires video camera, microphone and speaker for audio output.
- Touch: Requires a screen or monitor that supports multi-touch.
- Two-factor authentication: Requires use of PIN, biometric (fingerprint reader or illuminated infrared camera), or a phone with Wi-Fi or Bluetooth capabilities.
- Voice Typing: Requires a PC with a microphone.
- Wake on Voice: Requires Modern Standby power model and microphone.
- Wi-Fi 6E: Requires new WLAN IHV hardware and driver and a Wi-Fi 6E capable AP or router.
- Windows Hello: Requires a camera configured for near infrared imaging or fingerprint reader for biometric authentication. Devices without biometric sensors can use Windows Hello with a PIN or portable Microsoft compatible security key.
- Windows Projection: Requires a display adapter that supports Windows Display Driver Model (WDDM) 2.0 and a Wi-Fi adapter that supports Wi-Fi Direct.
Is Windows 11 worth it?
According to Microsoft’s current support plan, Windows 10 will lose support for future feature and security updates on October 14, 2025. After that date, any business, regardless of size, will incur a significant risk of liability for using Windows 10. With that in mind, upgrading to Windows 11 is obviously necessary and entirely worth the time and effort.
Windows 11 is designed to take advantage of the latest in both hardware and software security protocols, something Windows 10 is not able to do. These security measures help the operating system fend off various cyberattacks and malware including software viruses and ransomware. Because Windows 11 is a free upgrade to Windows 10, for most businesses and individuals there is little reason not to upgrade.
SEE: Here’s how to find and install the new Windows 11 22H2 update.






